Motivation: Electric Potential
- We wish to bring in a test charge from infinity to point ; is in the presence of an existing charge in space
- ’s electric field will try to repel ; we must do work to overcome the force exerted on and move
- How is work defined?
- All forces must have an equal and opposite reaction force; the force we exert to move must then be equal to ’s electric field, which is
- Then, the force we exert is
- ==Then, the work needed to move a point charge can be written as==
Procedure: Electric Potential to Move a Point Charge
- Electric potential is the work done per positive unit test charge as approaches 0
- is always defined assuming a positive test charge
- The reference point is infinity as convention
- As electric fields are conservative, we obtain the same electric potential no matter what path taken to get to ; the simplest path would always be a straight line from to
- ==If , then the positive test charge will be repelled and , so we are doing work against the electric field
- ==If , then the positive test charge will be attracted and , so the electric field is doing the work
Procedure: Electric Potential for Point and Charge Distributions
- The general equation we found for electric potential for a point is very flexible
Definition: Electrostatic Potential Energy
- Analogy: the gravitational potential at a point is the gravitational potential energy of a unit mass placed at that point
- The electric potential at any point in the electric field is the electric potential energy of a unit positive charge at that point
- Electric potential is amount of work needed to bring point charge from infinity to
- Electric potential energy is the energy needed to move a charge against the electric field
- Def:
- Negative means that work was done by the electric field
- Positive means that work was done against the electric field
Differential Length Review
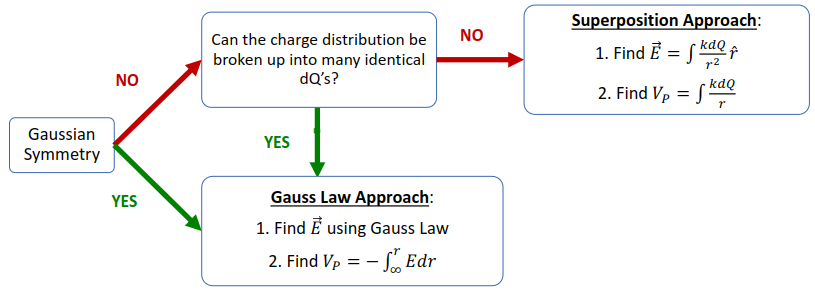
Electric Potential of Charge Distribution
- There are two methods of calculating the potential at :
Conceptual Tricks
Charge, Potential, E-field
- Because , the electric field always points in the direction of decreasing potential
- Change of potential energy is
- If is negative, the electric field is doing the work and ,
- If is positive, we (outside forces) are doing the work and ,
- Change of potential energy is the work done by an external agent; the electric field does opposite work
- Electric field has to be perpendicular to equipotential lines or surfaces
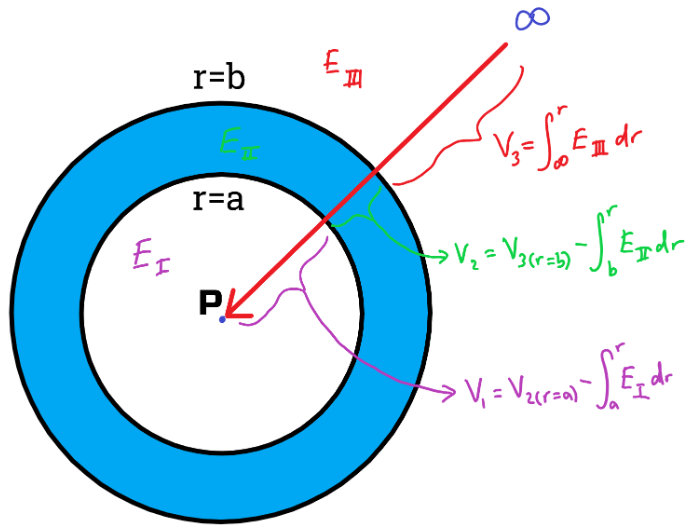
- When the question asks for “calculate potential for all r”, make sure to consider various cases of r, such as r larger than radius, smaller than radius, etc.